Multiagent AI frameworks provide for improved problem solving and the implementation of complex scenarios through the benefit of multiple perspectives. However this technology, while being a fantastic enabler, involves somewhat of a paradigm shift for traditional developers. What I mean is that as developers, while we consider business aplications from multiple perspectives, the actual build process is one dimensional. We write some code, probably get someone to check it and generally iterate on this process until we end up with something that delivers reasonable value (this is obviously a gross oversimplification). When we think about multagent frameworks, there is the potential to abstract a lot of this repetition as the application building stage and there is a shift to considering solutions from a meta perspective - that is a solution to create solutions.
I’ve already introduced multiagent frameworks, and if you’ve missed the post, you can read it here.
Improved problem solving using diverse perspectives
This approach mimics a human collaborative enviornment, where teams with varied expertise and viewpoints often ourperform individuals. Key aspects where this is highlighted are:
- Specialisation: AI agents can be designed with specialised knowledge and skills which allows for the effective division of labour and contributes unique strenghts.
- Complementary problem-solving strategies: Agents can use different algorithms and approaches to find optimal and novel solutions.
- Bias mitigation: Biases and hallucinations and well documented and the use of multiple agents can help counteract this by cross-checking and validating between agents to produce a more balanced outcome.
- Comprehensive problem analysis: A holistic exploration of the problem space can be performed with each agents focusing on various aspects.
- Dynamic adaption: Agents can learn from each other and adapt their strategies based on collective insights which leads to continuous improvements in problem solving capabilities.
- Robustness and resilience to failure: Agents are able to compensate for the failure of other agents and this redundancy enhances the overall reliability of the system.
The collaborative process between agents
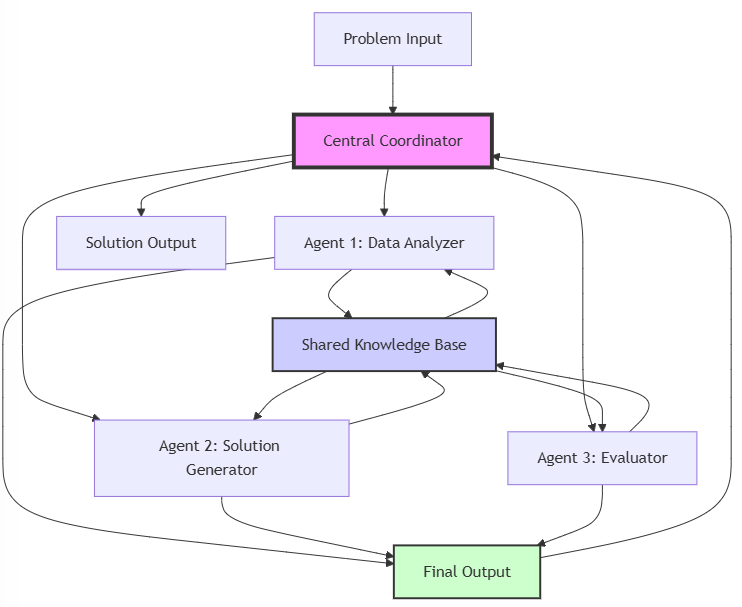
This diagram illustrates a simple multiagent framework with the following components:
- Central Coordinator: Acts as the main orchestrator, distributing tasks and managing the overall workflow.
- Agent 1 (Data Analyzer): Responsible for processing and analyzing input data.
- Agent 2 (Solution Generator): Generates potential solutions based on analyzed data and current knowledge.
- Agent 3 (Evaluator): Assesses the quality and feasibility of generated solutions.
- Shared Knowledge Base: A central repository where agents can store and access shared information, facilitating collaboration and learning.
- Final Output: Where agents collectively contribute to forming the solution.
- Solution Output: The final result after processing through the multiagent system.
The workflow in this diagram depicts:
- A problem is input into the system via the Central Coordinator.
- The Coordinator distributes tasks to the specialized agents.
- Agents perform their specific roles (analyzing, generating solutions, evaluating).
- All agents interact with the Shared Knowledge Base, updating and retrieving information.
- Agents contribute to the Final Output.
- The Final Output is sent back to the Coordinator for any necessary iterations.
- Once satisfied, the Coordinator produces the Solution Output.
This diagram demonstrates how multiple agents with diverse roles can interact and collaborate within a framework to solve complex problems. The Shared Knowledge Base is crucial as it allows agents to learn from each other and maintain a collective intelligence.
3. Comparison of Multiagent AI Frameworks: MetaGPT, Microsoft AutoGen, LangChain, and AgentVerse
1. MetaGPT
MetaGPT is a multi-agent system where various GPT-powered agents (Product Managers, Engineers, Architects, etc.) collaborate to complete complex tasks such as software development and project management. Key features include:
- Role-based Collaboration: Different agents handle specific roles in the software development process, ensuring a smooth workflow. For example, one agent might focus on the front-end code while another works on API development.
- Precompilation and Error Detection: MetaGPT introduces precompilation mechanisms, allowing early error detection, which is crucial in reducing time spent debugging.
- Scalability: MetaGPT is scalable, capable of handling large-scale enterprise applications by simulating the functions of an entire software company.
2. Microsoft AutoGen
Microsoft AutoGen is designed for enterprises with complex workflows and integrates tightly with Microsoft’s cloud and enterprise services. It emphasizes structured workflows and supports human-in-the-loop interactions, allowing for adjustments and real-time feedback during AI operations.
- Seamless Cloud Integration: Built to work with Azure, making it a natural choice for enterprises already using Microsoft’s cloud.
- Human-Agent Interaction: AutoGen facilitates collaboration between human experts and AI agents, with a focus on task management and optimization.
3. LangChain
LangChain is a flexible framework designed for chaining together various language model APIs. It focuses more on modularity and allows developers to create custom applications by leveraging different components, such as data processing, API interaction, and logic handling.
- Modularity: LangChain’s modular approach makes it ideal for building applications that require fine-tuning or integration with other APIs.
- Less Structured Collaboration: While LangChain supports multiple agents, it does not provide the same depth in role-based task assignments as MetaGPT.
4. AgentVerse
AgentVerse is also a multi-agent framework focused on collaboration but with built-in code review features, making it useful for development projects.
- Code Review: One of its standout features is the built-in code review mechanism, which allows agents to check each other’s work before final output.
- Enhanced Debugging: While both MetaGPT and AgentVerse support debugging, MetaGPT’s precompilation feature offers a slight edge by catching errors earlier in the development process.
Key Differences:
- MetaGPT is more focused on creating a collaborative software development team with agents handling specific roles, making it ideal for end-to-end project execution.
- Microsoft AutoGen is best suited for cloud-based, enterprise-level operations with seamless human-AI collaboration.
- LangChain is highly modular, allowing more flexibility in creating bespoke applications but lacks the structured role assignment found in MetaGPT.
- AgentVerse shares MetaGPT’s focus on collaboration but adds robust debugging and code review capabilities.
Additional Resources:
- MetaGPT GitHub Repository for setup instructions and detailed usage.
- Microsoft AutoGen Documentation for enterprise-focused workflows.
- LangChain Documentation for flexible AI application development.
- AgentVerse Documentation for a focus on collaborative debugging.